First Law Of Thermodynamics Definition

In any irreversible.
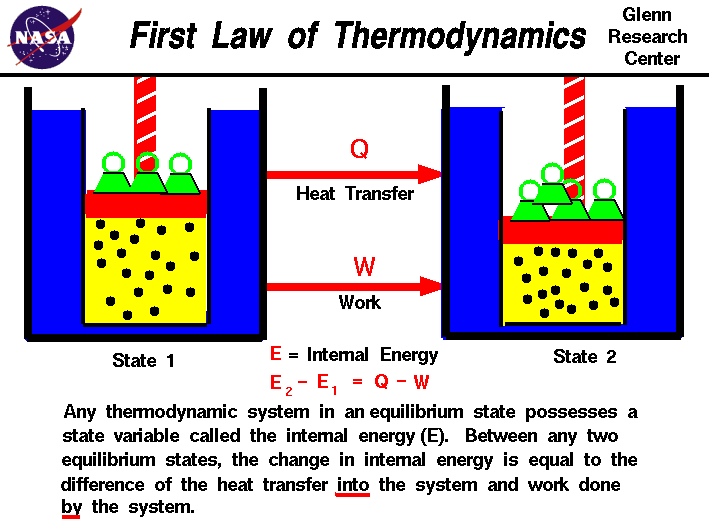
First law of thermodynamics definition. The law forms the basis of the principle of conservation of energy. The first law of thermodynamics states that the heat added to the system adds to its internal energy while the work done by the system reduces the internal energy. The first law of thermodynamics defines the internal energy e as equal to the difference of the heat transfer q into a system and the work w done by the system. Any of three principles governing the relationships between different forms of energy.
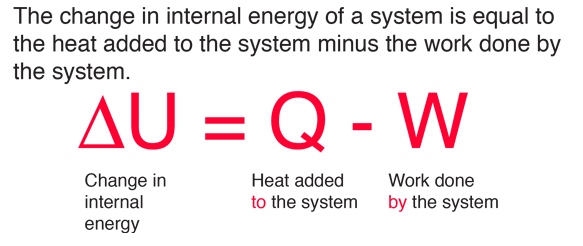
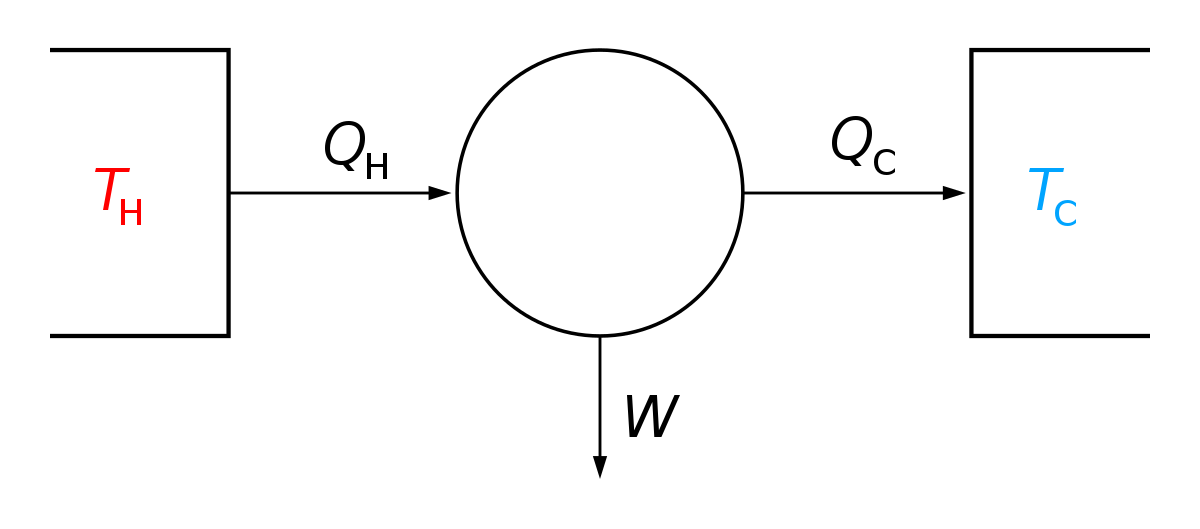
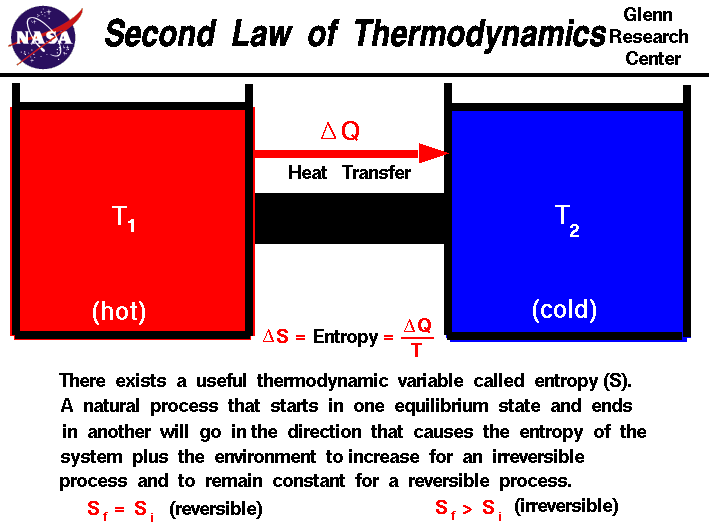
In symbols you use u to denote the change in internal energy q to stand for heat transfer and w for the work done by the system and so the first law of thermodynamics is. The second law of thermodynamics states that heat cannot be transferred from a colder to a hotter body within a system without net changes occurring in other bodies within that system. Here is a statement of first law of thermodynamics. In other words the total energy of the universe remains constant.
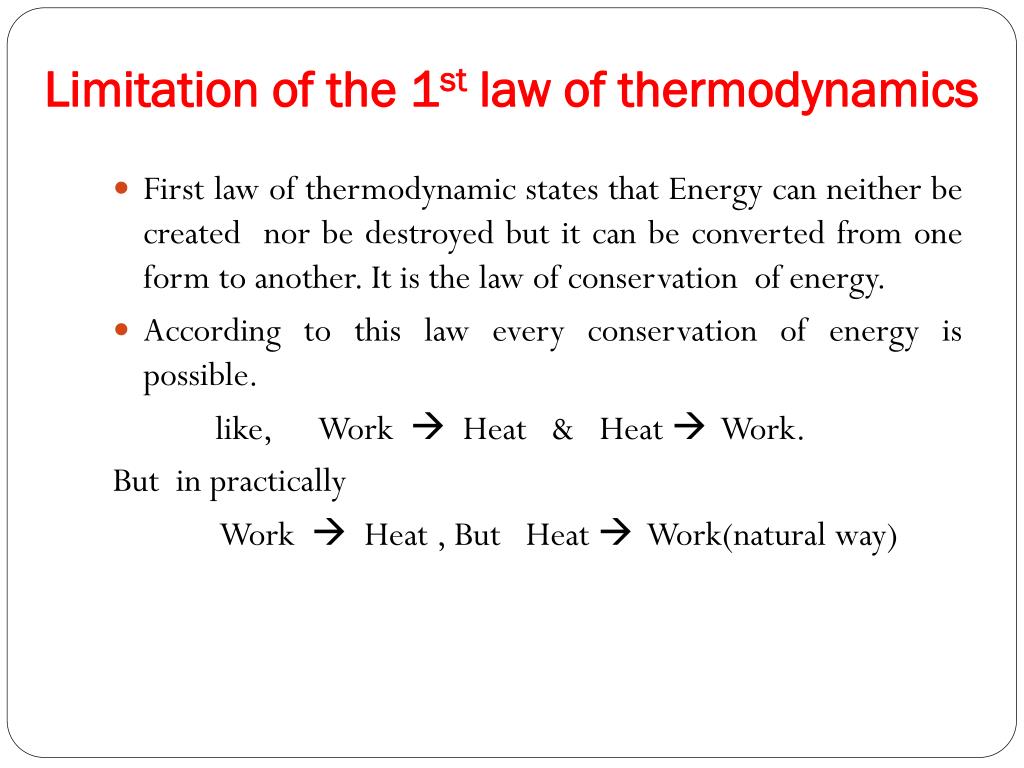
The first law of thermodynamics is the physical law which states that the total energy of a system and its surroundings remain constant. The energy can just be transformed from one form to another. Even we cannot destroy any energy. This statement definition of first law wants to say that we cannot create any energy.
It can changed only from one form to another. The very first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Heat removed from a system would be assigned a negative sign in the equation. Energy can neither be created nor can be destroyed but the transformation of one form into another form can be possible.
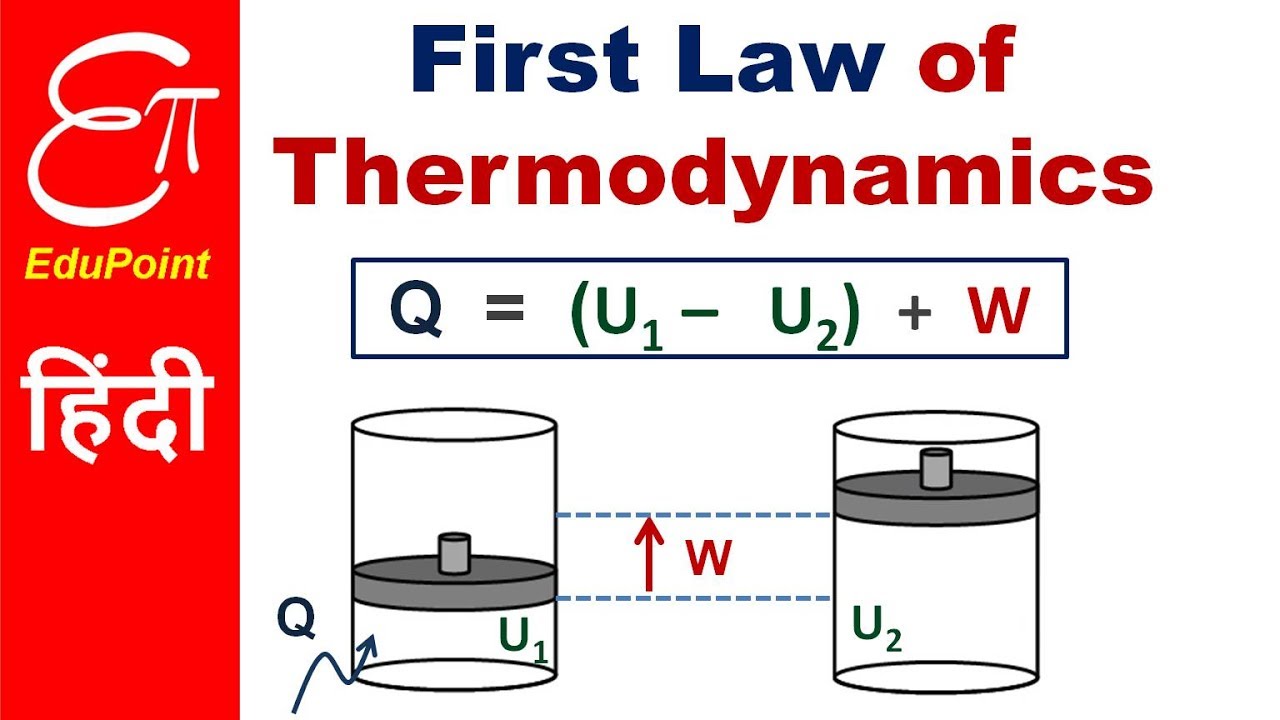
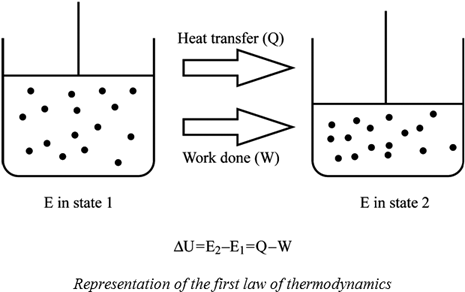
First law of thermodynamics. The first law of thermodynamics law of conservation of energy states that the change in the internal energy of a system is equal to the sum of the heat added to the system and the work done on it. The law is also known as the law of conservation of energy which states energy can transform from one form into another but can neither be created nor destroyed within an isolated system. The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy adapted for thermodynamic processes distinguishing two kinds of transfer of energy as heat and as thermodynamic work and relating them to a function of a body s state called internal energy.
U q w. This means that anything that uses energy is changing the energy from one kind of energy to another. The first law is put into action by considering the flow of energy across the boundary separating a system from its surroundings. E2 e1 q w we have emphasized the words into and by in the definition.
The laws of thermodynamics are deceptively simple to state but they are far reaching in their consequences.