First Law Of Thermodynamics Physics Definition
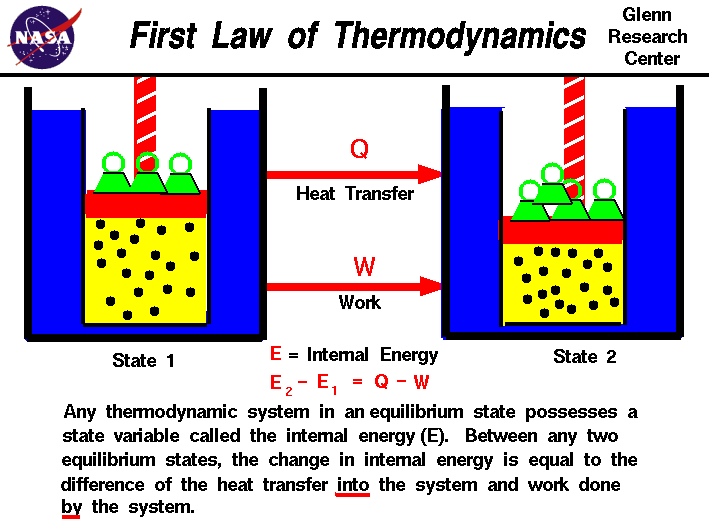
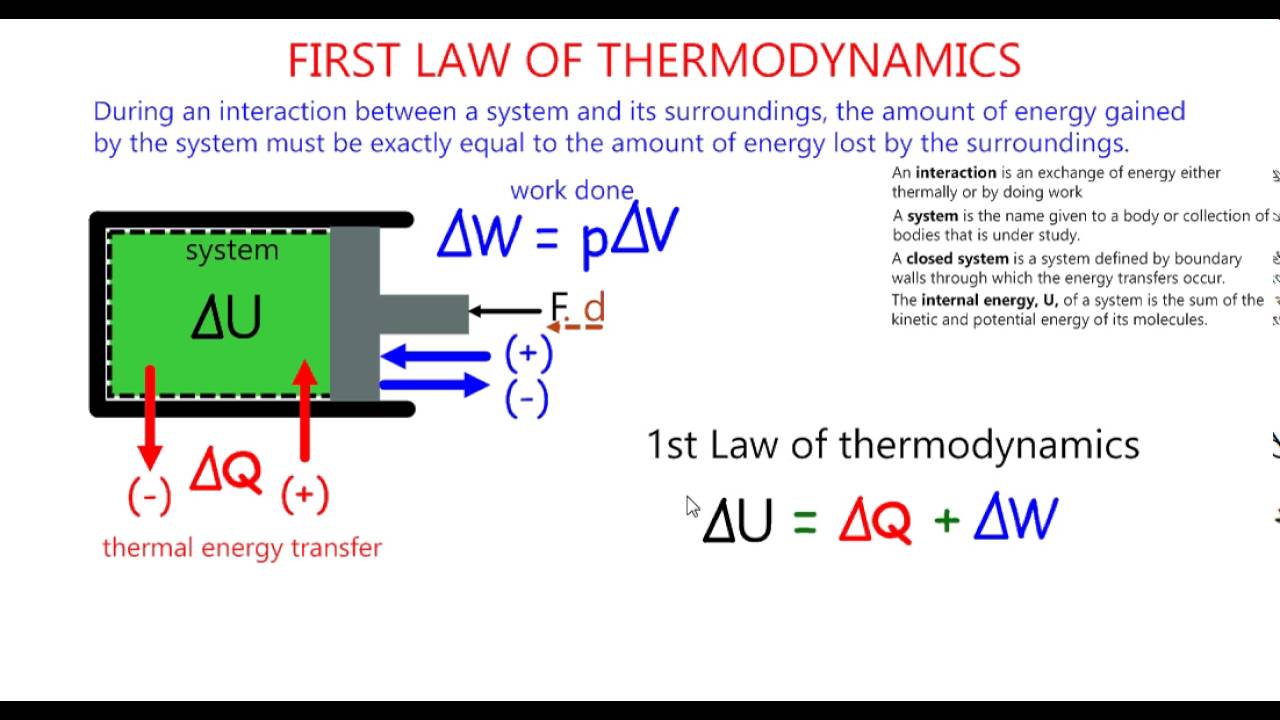
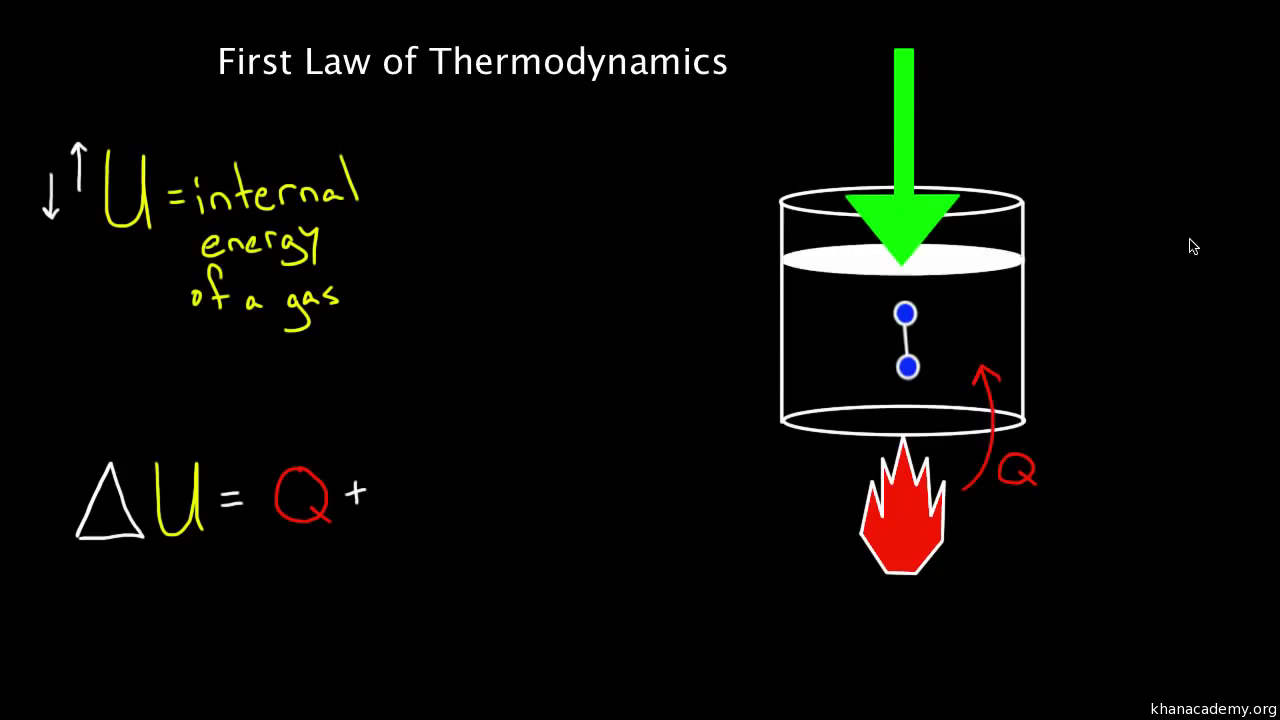
The first law of thermodynamics defines the internal energy e as equal to the difference of the heat transfer q into a system and the work w done by the system.
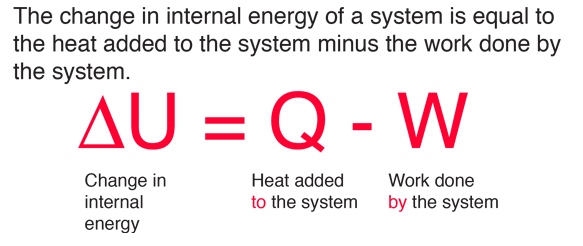
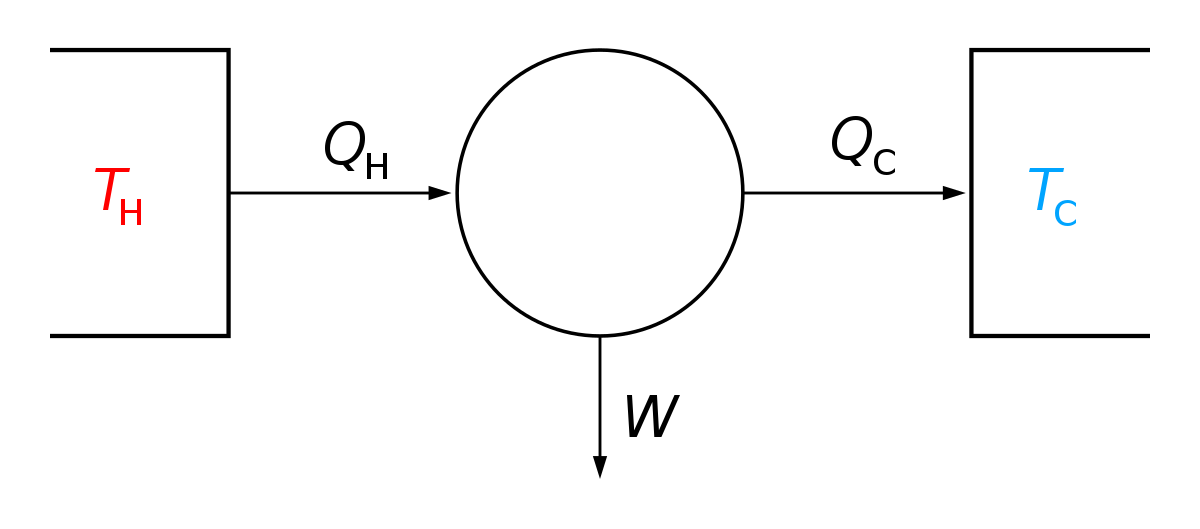
First law of thermodynamics physics definition. The first law of thermodynamics applies the conservation of energy principle to systems where heat transfer and doing work are the methods of transferring energy into and out of the system. The first law of thermodynamics is one of the physical laws of thermodynamics other are zeroth law 2nd law and 3rd law that states that heat is a form of energy and the total energy of a system and it s surrounding remained conserved or constant. The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy adapted for thermodynamic processes distinguishing two kinds of transfer of energy as heat and as thermodynamic work and relating them to a function of a body s state called internal energy. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy for a system is equal to the heat transfer to the system minus the work done by the system on its surroundings.
First law of thermodynamics the fundamental principle of physics that the total energy of an isolated system is constant despite internal changes conservation of energy law of conservation of energy. Or in more simple terms for an isolated system. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system. Heat removed from a system would be assigned a negative sign in the equation.
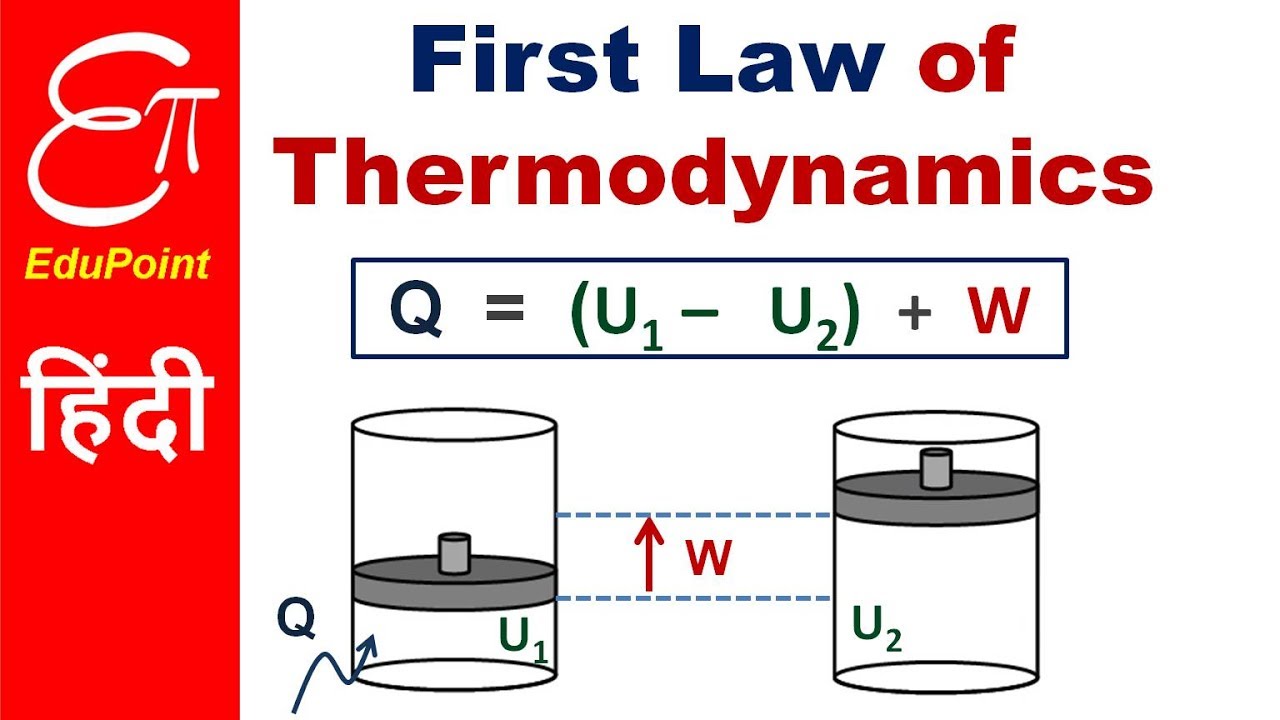
The first law of thermodynamics is a general result that is thought to apply to every process in nature which proceeds between equilibrium states it tells us that energy must be conserved in every process but it does not tell us whether any process that conserves energy can actually occur. E2 e1 q w we have emphasized the words into and by in the definition. The first law of thermodynamics is given as δu q w where δu is the change in internal energy of a system q is the net heat transfer the sum of all heat transfer into and out of the system and w is the net work done the sum of all work done on or by the system.