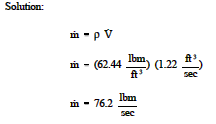Mass Flow Rate Equation Thermodynamics

The above equation is only true for a flat plane area.
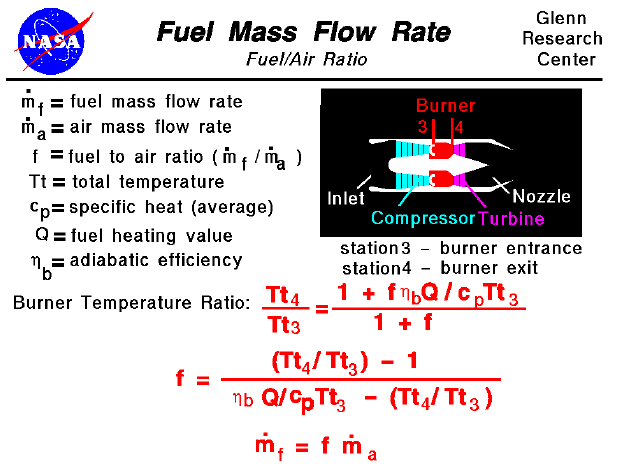
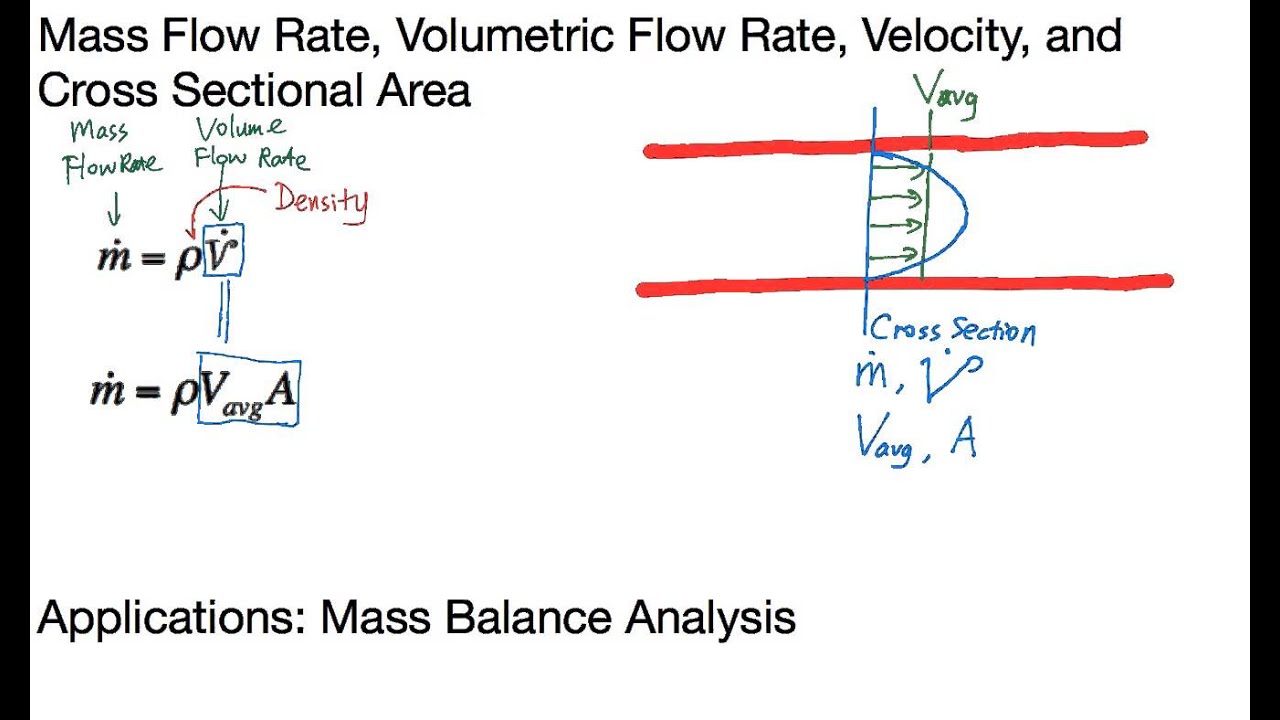
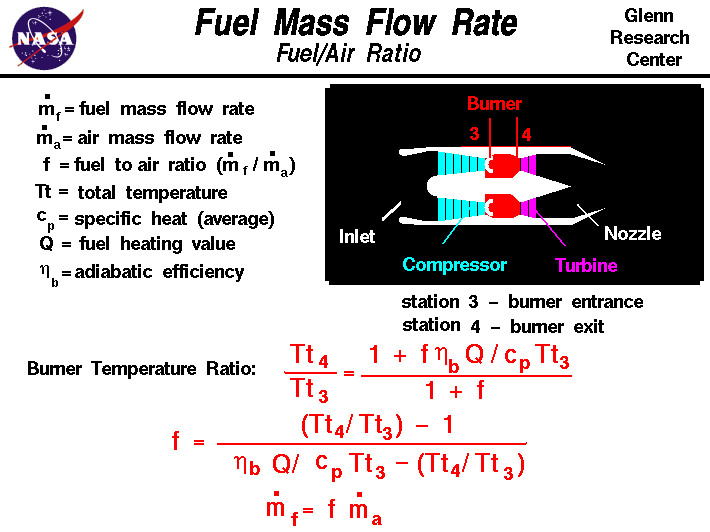
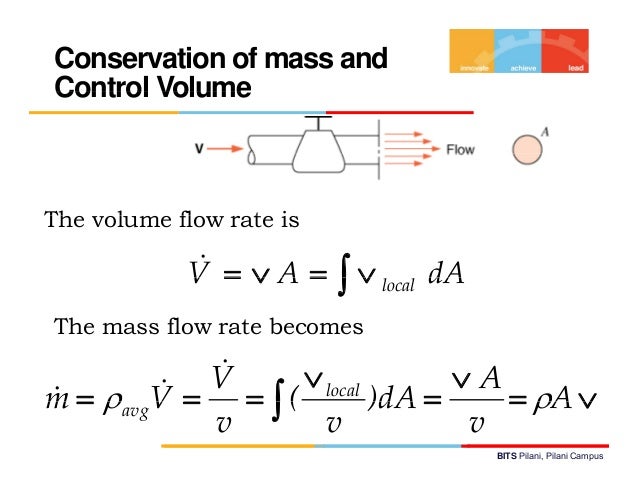
Mass flow rate equation thermodynamics. The mass flow rate of a fluid flowing in or out of a pipe or duct is proportional to the cross sectional area a of the pipe or duct the density of the fluid ρ and the velocity of the flow v. In general including cases where the area is curved the equation becomes a surface integral. Solve for the mass flow rate. Therefore the mass flow rate.
A area of cross section. The mass flow formula is given by m ρva. A cross sectional area for flow. V flow velocity of the mass elements.
A cross sectional vector area surface. Under steady flow conditions there is no mass or energy accumulation in the control volume thus the mass flow rate applies both to the inlet and outlet ports. The flow rate through a differential area da is. Equations for determing the mass flow rate.
Furthermore with a constant mass flow rate it is more convenient to develop the energy equation in terms of power kw rather than energy kj as was done previously. Where. ρ density of fluid v velocity of the liquid and. D ρ v n da.
Or q volume flow rate ρ mass density of the fluid. Can be determined using. Formula of mass flow rate.